- May 09, 2024
- 845 Views
- 0 Comments
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals in various ways. While the core features of ASD include challenges in communication and social interaction, many individuals with autism also struggle with executive functioning skills. Executive functioning refers to a set of cognitive processes that help us plan, organize, initiate, complete tasks, and regulate our emotions and behavior. These skills are crucial for success in academics, employment, and daily life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the relationship between autism and executive functioning and provide valuable strategies for individuals with ASD, their families, and educators to promote success.
Understanding Executive Functioning
Before delving into strategies, it's essential to have a clear understanding of executive functioning and how it manifests in individuals with autism.
Components of Executive Functioning
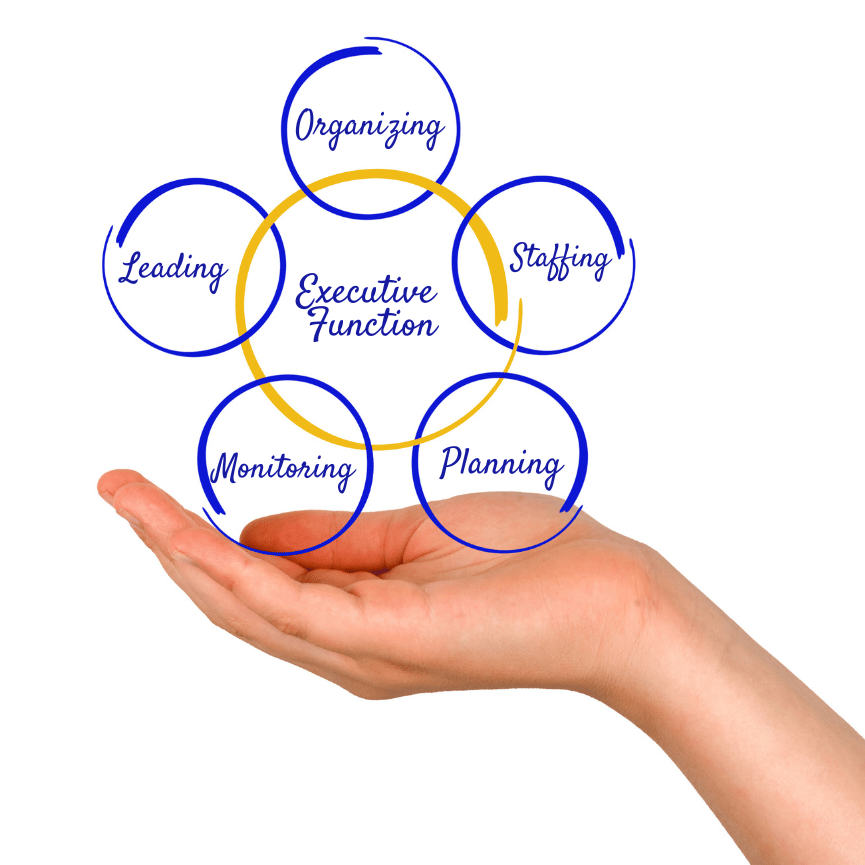
Executive functioning encompasses several interconnected components, including:
- Inhibition: The ability to control impulses and maintain focus on a task.
- Working Memory: Holding and manipulating information in one's mind while working on a task.
- Flexibility: Shifting between tasks or adapting to changes in a plan.
- Planning and Organization: Setting goals, making plans, and breaking them into manageable steps.
- Initiation: Starting tasks independently without procrastination.
- Emotional Regulation: Managing emotions and reactions in various situations.
- Time Management: Allocating time effectively for tasks and activities.
Executive Functioning Challenges in Autism
Many individuals with autism face difficulties in one or more areas of executive functioning. These challenges can significantly impact their daily lives, making it essential to develop effective strategies.
Strategies for Success
Now that we have a foundation in understanding executive functioning in the context of autism, let's explore practical strategies to support individuals on the spectrum in developing these crucial skills.
Visual Supports and Schedules
Visual aids can be powerful tools for individuals with autism, helping them grasp concepts, routines, and schedules more easily. Consider using visual schedules, social stories, and visual cues to enhance understanding and predictability.
- Visual Schedules: Create visual schedules that outline daily routines or task sequences. These schedules can be customized to fit individual needs and preferences. Visual schedules offer a clear visual representation of what to expect, reducing anxiety and enhancing executive functioning.
- Social Stories: Social stories are short narratives that explain social situations and expectations. They can help individuals with autism better understand and navigate various social contexts, improving their emotional regulation and social interactions.
Task Breakdown and Simplification
Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps can make a significant difference in executive functioning for individuals with autism.
- Task Analysis: Analyze complex tasks and identify each step involved. Create a checklist or visual representation of the steps to provide clarity and guidance.
- Chunking: Group related information or tasks together. This can simplify information processing and make it easier to manage.
Use of Visual and Auditory Reminders
Visual and auditory reminders can help individuals with autism remember tasks, appointments, and responsibilities.
- Visual Reminders: Use sticky notes, timers, or alarms to provide visual cues for upcoming tasks or transitions.
- Auditory Reminders: Set auditory alerts on electronic devices to signal task changes or important events. These reminders can help with time management and task initiation.
Establishing Routines and Consistency
Routine and predictability are essential for individuals with autism to improve executive functioning skills.
- Consistent Schedules: Maintain a consistent daily routine whenever possible. Knowing what to expect at specific times can reduce anxiety and improve time management.
- Visual Routine Charts: Create visual routine charts that outline the daily schedule. Include icons or images to represent each activity, making it easier for individuals with autism to follow the routine.
Social Skills Training
Social skills are a vital component of executive functioning, as they involve emotional regulation and adapting to social situations.
- Social Skills Groups: Enroll individuals with autism in social skills groups or therapy sessions where they can learn and practice social interaction skills in a supportive environment.
- Role-Playing: Use role-playing exercises to simulate real-life social situations and teach appropriate responses and strategies for managing emotions during interactions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a therapeutic approach that can help individuals with autism improve emotional regulation and problem-solving skills.
CBT Techniques: Work with a trained therapist to learn and apply CBT techniques that can enhance executive functioning, including identifying and challenging irrational thoughts and developing coping strategies.
Assistive Technology
Leveraging technology can be a valuable strategy to support executive functioning skills.
- Task Management Apps: Explore task management apps that provide reminders, to-do lists, and organization features. These apps can help individuals with autism stay on top of their responsibilities.
- Text-to-Speech and Speech-to-Text Tools: Assistive technology tools like text-to-speech and speech-to-text applications can assist with written communication, making it easier to express thoughts and ideas.
Collaborate with Educators and Therapists
Effective collaboration between parents, educators, therapists, and individuals with autism is essential for implementing and reinforcing these strategies.
- Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): Collaborate with schools to create IEPs that address the specific executive functioning challenges of each student with autism. These plans can provide tailored support and accommodations.
- Regular Communication: Maintain open lines of communication between home and school environments to ensure consistency in implementing strategies.
Supporting individuals with autism in developing executive functioning skills is essential for their overall success and quality of life. By using a combination of visual supports, task breakdown, reminders, routines, social skills training, therapy, assistive technology, and collaboration with educators and therapists, individuals with autism can significantly improve their executive functioning abilities. It's important to remember that every person with autism is unique, and strategies should be personalized to meet their individual needs and strengths. With patience, understanding, and targeted support, individuals with autism can thrive and achieve their full potential.



Post Your Comment